INTRODUCTION
Stomata are small pores like structure present in the epidermis layer of plants.
They are absent in Roots, Saprophytic and Parasitic plants.
In floating plants, they are non-functional and confined to upper epidermis only, while in terrestrial plants having dorsiventral leaves, stomata are on the lower epidermis, in isobilateral leaves they are present on both upper and lower epidermis.
Stomata can be present:
- At the level of epidermis
- Below epidermis in stomal pits
- Above epidermis as raised stomata.
The main function of stomata is TRANSPIRATION means exchange of gases like CO2 from atmosphere enters and O2 leaves through it as well as Exchange of Water vapors.
The opening and closing of stomata are due to Turgor Pressure.
Increase in Turgor Pressure leads to Opening of Stomata.
In most of the plant's stomata opens during Day and Closed at night such stomata are called as Photo active.
In other plants including CAM plants (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) stomata opens at night and closed in day, this is called as Scotoactive.
STRUCTURE OF STOMATA
- Stomata consist of a pair of specialized cells called as Guard Cells that have the ability to change shape accordingly. These Guard Cells are attached to each other unless and until stomata have to open. Guard cells differ from epidermal cells in having chloroplast.
- Guard cells contain dense protoplasm and numerous organelles.
- The outer wall of guard cells is thin, and inner wall is thicker that resist stretching.
- Cellulose microfibrils are radially arranged in inner wall of guard cells.
- Guard cells are sensitive to Light, Humidity and some Plant Growth Regulators like Abscisic Acid (ABA)
- When stomata open, a pore is formed called as Stoma.
- The adjacent cells around Guard cells are called as Subsidiary Cells.
- Guard cells along with Subsidiary Cells are called as Stomatal Complex.
OPENING and CLOSING of Stomata
- Opening of stomata is initiated by transport of Potassium ion into Guard cells from neighboring Subsidiary Cells
- This leads to entry/influx of water into the guard cells by osmosis this leads to swelling of Guard Cells.
- Potassium slowly diffuses out and thus stomata close.
TYPES OF STOMATA
1.Kidney Shaped:
The walls of guard cells near to the pore is thicker and opposite wall is thinner
2,Dumbbell Shaped:
Mostly in Monocots (Grass Family and Cyperaceae)
They are named as Dumbbell because of the shape of guard cells, they have thick walls in center and thin walled at ends.
QUESTION PRACTICE:
Which of the following is surrounded by Guard Cells? (DSSSB Exam)
Xylem
Stomata
Phloem
Subsidiary Cells
Stomata in the leaves open and close due to
Circadian Rhythm
Genetic clock
Pressure of gas inside the leaves
Turgor pressure of guard cells
Choose the options that are correct match for the items in column 1 with Column II
a)ii b)i c)iv d)iia)ii b)i c)iv d)iii
a)i b)ii c)iii d)iv
a)iii b)iv c)i d)ii
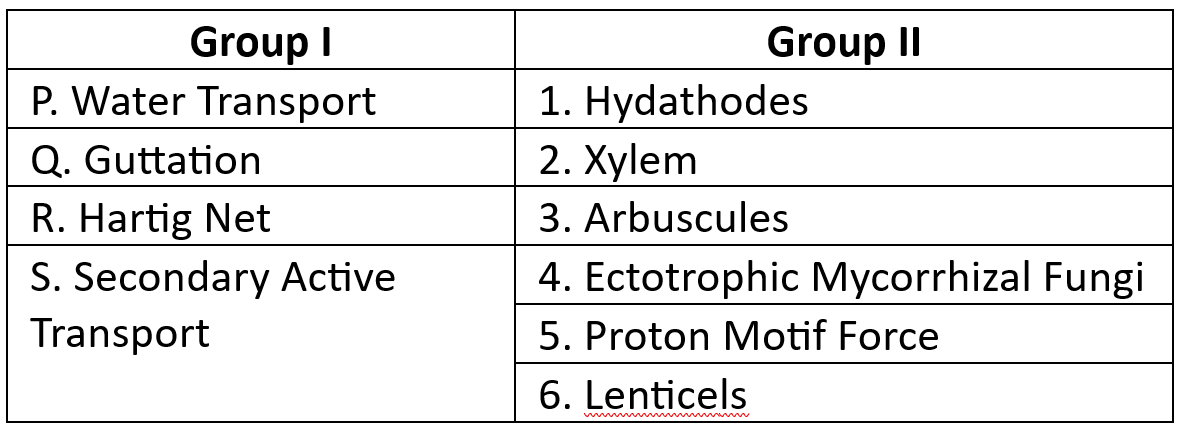
Match the correct options: (GATE-XL)
P.2 ,Q.1 ,R.4 ,S.5P.1 ,Q.6 ,R.5 ,S.2
P.2 ,Q.6 ,R.4 ,S.5
P.6 ,Q.4 ,R.1 ,S.3
Opening and closing of stomata is controlled by (UP PGT)
Ferric ion
Potassium ion
Magnesium ion
Zinc ion
The Rate of Transpiration will be very less in a situation where (KVS)
Environment is very hot and dry
Ground water is available in plenty
Wind is blowing
Relative humidity is very high
Select the incorrect statement from the following regarding Transpiration in plants
Create Transpiration pull for absoption and transport of organic metabolites from the soil
Transports minerals from soil to aerial parts of the plant
Phloem is conduit for transport of water that gets transpired by leaves
Cohesion and Adhesion properties of water are essential for transpiration pull
A and D only
C and B only
A and C only
C and D only
Out of the following statements, which one is not correct ? (ICAR PG Agronomy 2022)
1. Number of stomata found in all different leaves is different in plants
2. Distribution of stomata is different in different plants
3. Distribution, number, size and type of stomata are same in every plant
4. Size and type of stomata is different in different plants
Which one in incorrect with respect to transpiration in plants (ICAR PLANT SCIENCE 2022)
1. Flow of mineral nutrients and water through xylem
2. Diffusion of carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis
3. Change in osmotic pressure of cells
4. Reduction of cooling effect on the leaf surface
Light is the signal that controls stomatal movement in plants. Stomatal movement is stimulated by (ICAR PG 2020 Plant Biotechnology)
Red Light
Blue Light
Green Light
Yellow Light


Comments
Post a Comment