MEANING
Resins are plant exudates-materials composed largely by terpenoids, phenolic compounds (coumaric, caffeic, and ferulic acids), with few fatty acids and glycerides.
Where are they formed?
- They may be formed within plastids present in epithelial cells of plants or even synthesized in spherosomes, both in resin duct cells and in parenchymal cells.
- Spherosomes are single membrane bound small organelles that takes part in lipid storage.
Why are they formed?
- Secreted by plant in response to injury.
- They serve as a protective covering for wound.
Properties of Resins
- Resins are Volatile initially: They are fluid at fist due to volatile oil but the resinous sap solidifies on exposure to the air, partly through evaporation of the volatile constituent and partly through its oxidation. Finally, it may become hard and brittle.
- Resins are mixture of Hydrocarbons: Resins are mixtures of several different oxidized hydrocarbons which are poor in oxygen and rich in hydrogen and carbon.
- Resins are Inflammable (lacks O), due to their large proportion of carbon, burning with a sooty flame.
- Resins are insoluble in water; but are mostly soluble in the other liquids like ether, alcohol, carbon bisulphid, and oils.
- Oleoresins: When a considerable amount of volatile oil is associated with a resin the mixture (commonly of a honey-like consistency as in the turpentine of pines and firs) is distinguished as an oleoresin.
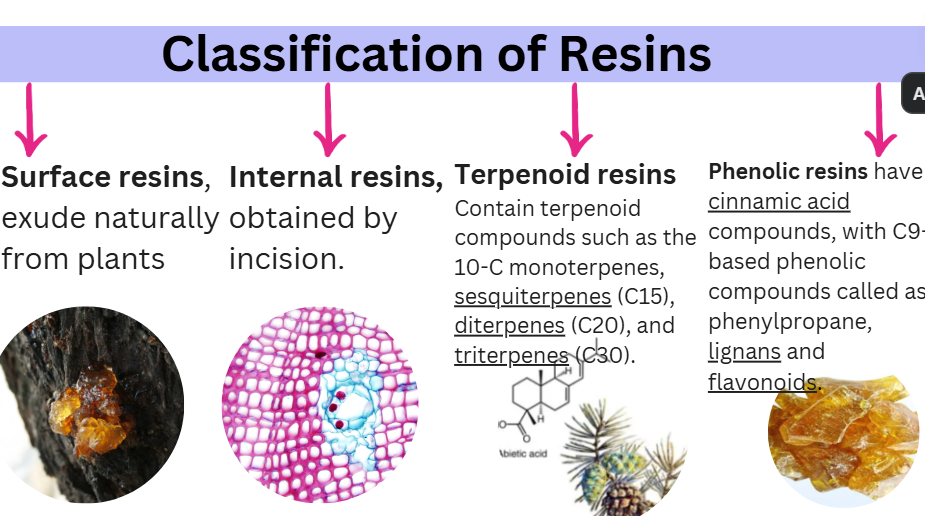
CLASSIFICATION OF RESINS
Uses of Resins
- Certain resins like humulus (flavoring agent-used in beer production)
- Cistus a resin (perfume fixative)
- Parthenium (rubber substitute)
- Euphorbia (fuel) are used commercially for medicinal purposes
- Balsams are soft, initially malleable, and therefore can be used an ointment in wound healing.
- Amber: Amber is a fossilized tree resin of gymnosperm plants with a rather heterogeneous composition. It is a polymeric structure.
GUMS
- Natural gums are hydrophilic carbohydrate polymers of high molecular weights, generally composed of monosaccharide units joined by glycosidic bonds.
- These polysaccharides have the ability to thicken as a result of both hydrogen bonding.
- They are soluble in water, which can form gels and mucilage’s.
- The true gums are either soluble in water or absorb it indefinitely; while they are insoluble in ether, alcohol, carbon bisulphid, and oils.
- Sometimes a gum and a resin are intimately united, forming what is known as a “ gum-resin ” .Example: asafetida







Comments
Post a Comment