- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Economic Botany- Morphology of Ashwagandha Plant
Botanical
Name: Withania somniferum
Family:
Solanaceae
Common Name:
Ashwagandha
Importance :
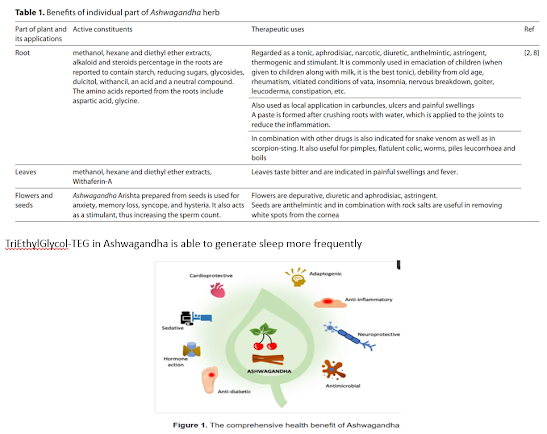
Main active constituents are ‘somniferum’ and withananine’. This is used as a tonic in geriatrics, being efficacious in relieving hand and limb tremors of elderly persons. It is considered as an aphrodisiac and rejuvenator and given for all kinds of weaknesses and is supposed to promote strength and vigour. Several preparations related to nervous systems contain the drug of this plant. Roots yield important drugs useful in all types of skin lesions, paralytic conditions, ulcers, in reducing pus formation and in rheumatic pain inflammation of joints.
The raw material used in medicine is the root, and the name “Ashwagandha” is derived from the word “ashwa”, meaning horse.
It is believed that after consuming the root, one gains powers similar to that of a horse. The second part of the name “gandha,” means fragrance and refers to the characteristic smell of the fresh root of the plant.
Morphology of Plant
It is a small, woody shrub in the
Solanaceae family that grows about two feet in height. Withania somnifera is an erect, evergreen (green in
whole year), branching, short shrub. The plant is usually clothed with minutely
stellate tomentum.
ROOTS:
The roots of Ashwagandha are fleshy when
dry, they are
straight, cylindrical, tapering
down, gradually unbranched of about 10-17.5cm long and 6-12milimeter diameter
in thick. The main roots are brownish outer and creamy interior and bear
fiber similar secondary
roots having acrid
taste and biter. Roots
are stout, fleshy and whitish
brown in colour.
STEM:
The stems of Withania are
brownish dark colour and erect, sometimes leaves are absent or less on lower part of stem.
Leaves are simple, petiolate with the leaf blade varying in
shape from elliptic-ovate to broadly ovate, entire
along margins, acute to obtuse at
apex, oblique at base. Leaves on vegetative shoot are alternate and
large and those on floral branches are opposite, arranged somewhat laterally in
pairs of one small leaf and one large leaf.
Infloroscence is cymose bearing in
the axil of large and small leaves as cymose cluster of 4-25 inconspicuous pale
green with monoceous flowers.
Seeds are normally many, discoid,
reniform and yellow.
It produces flowers indeterminately
round the year with a peak of flowering between March and July or throughout
the year. Berries start maturing in June-july.
Uses:

Comments
Post a Comment